Relays (Power Distribution)
102 products
Showing 1 - 48 of 102 products
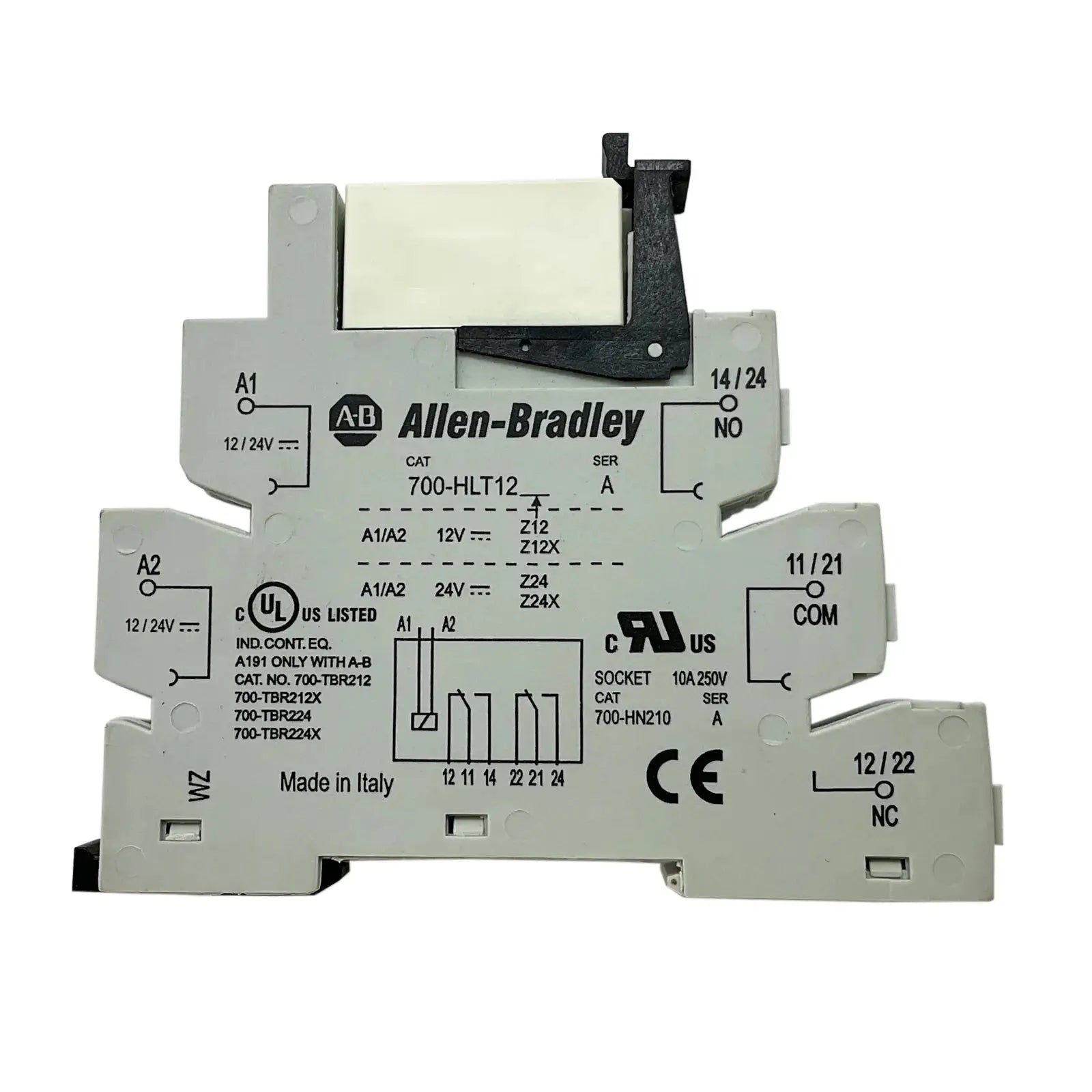
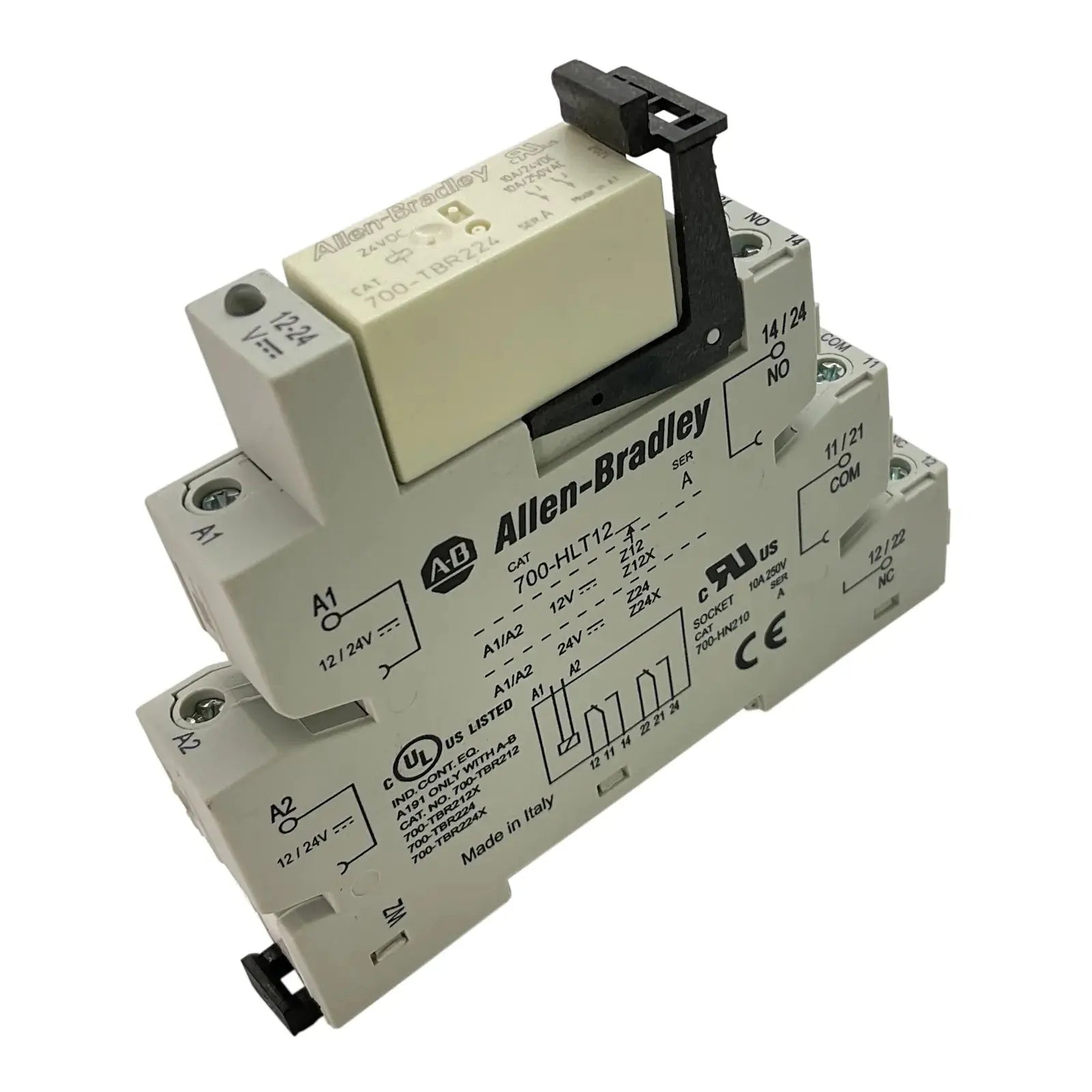
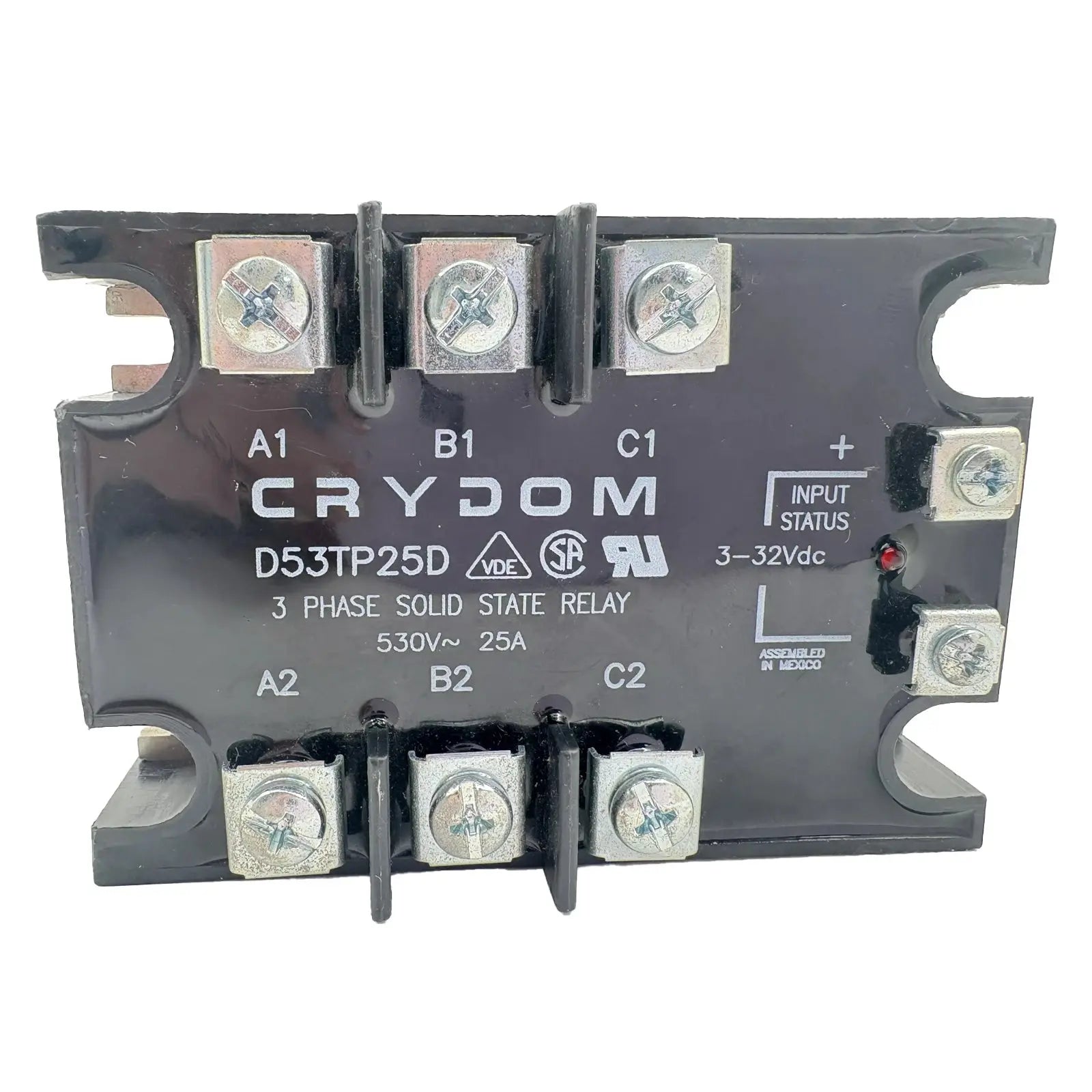
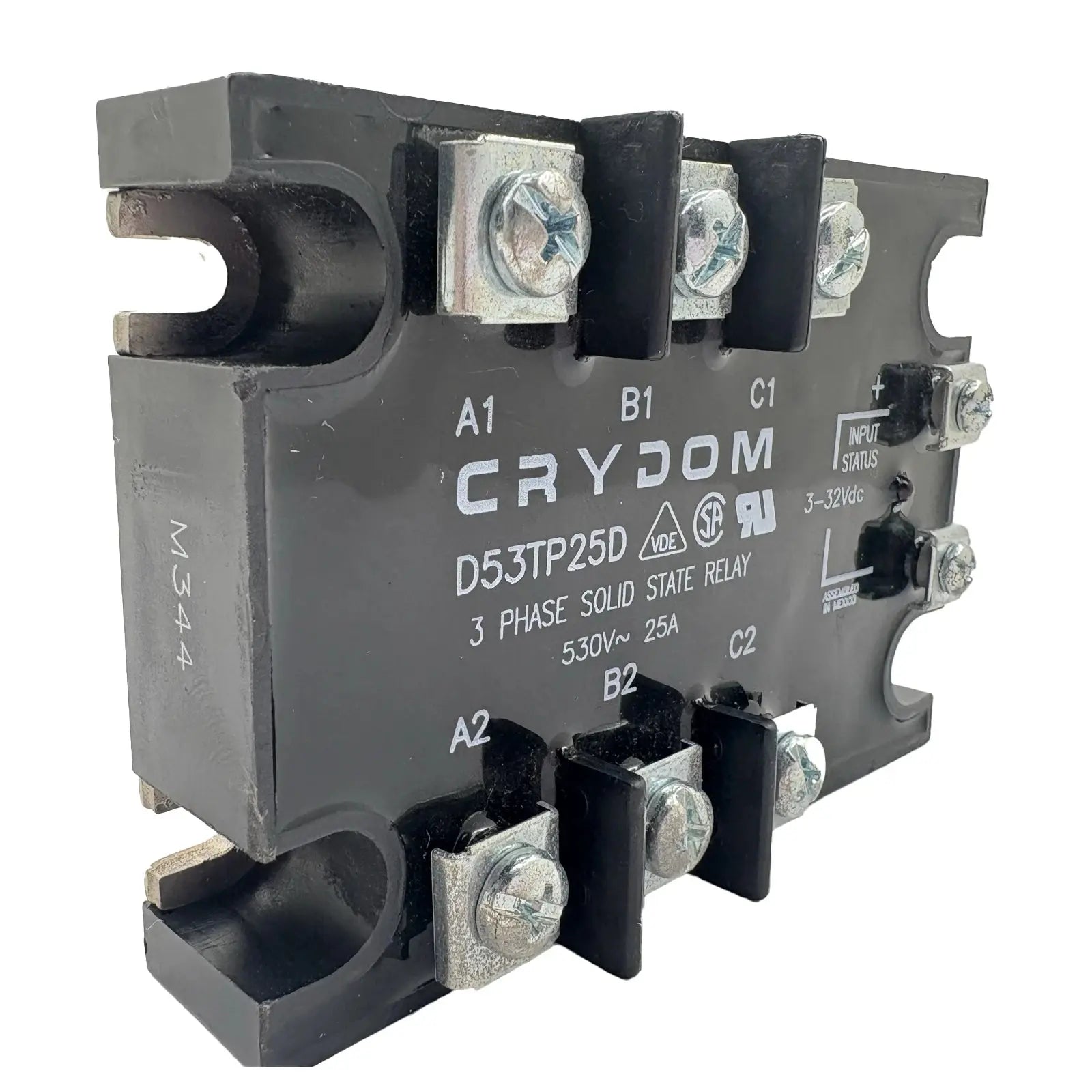
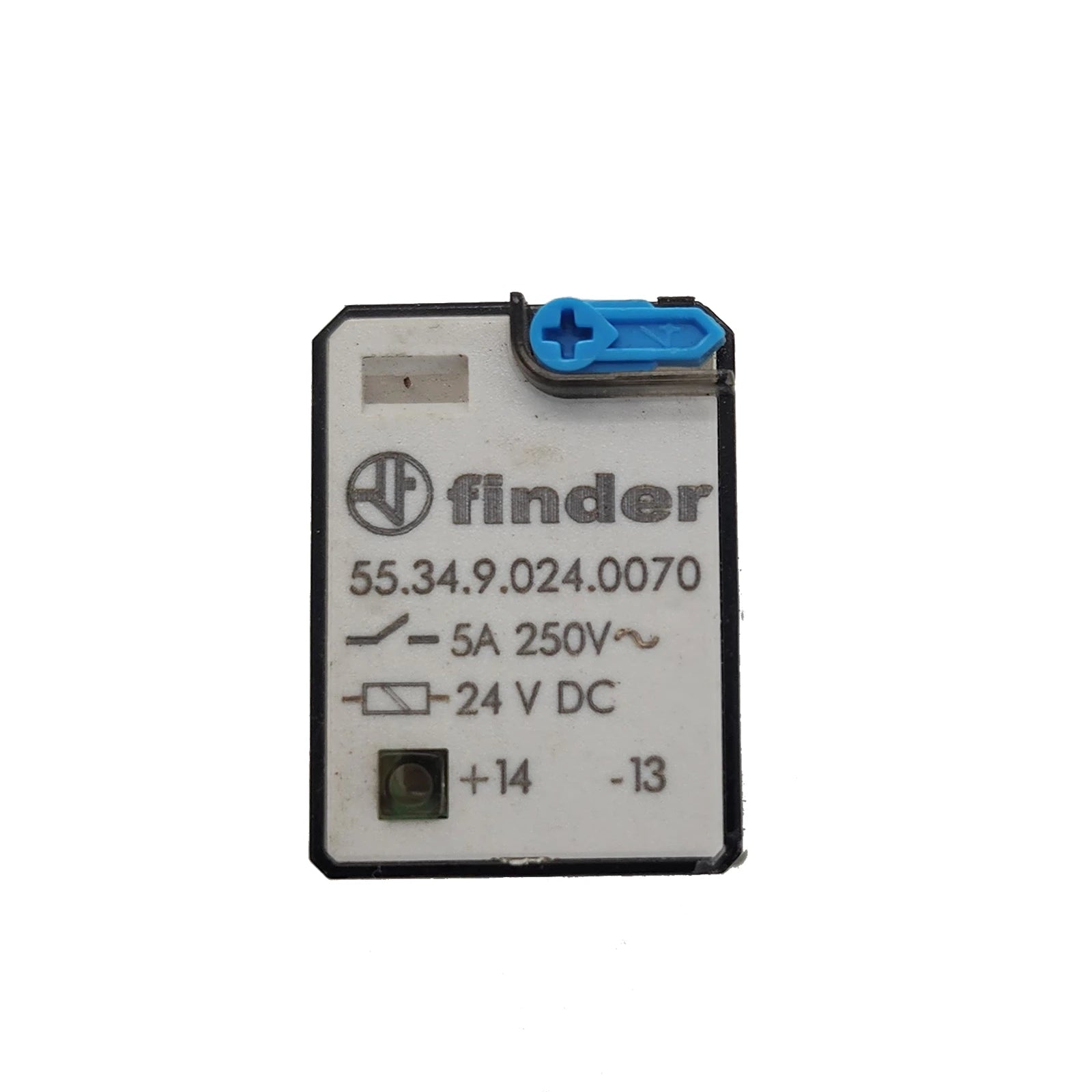
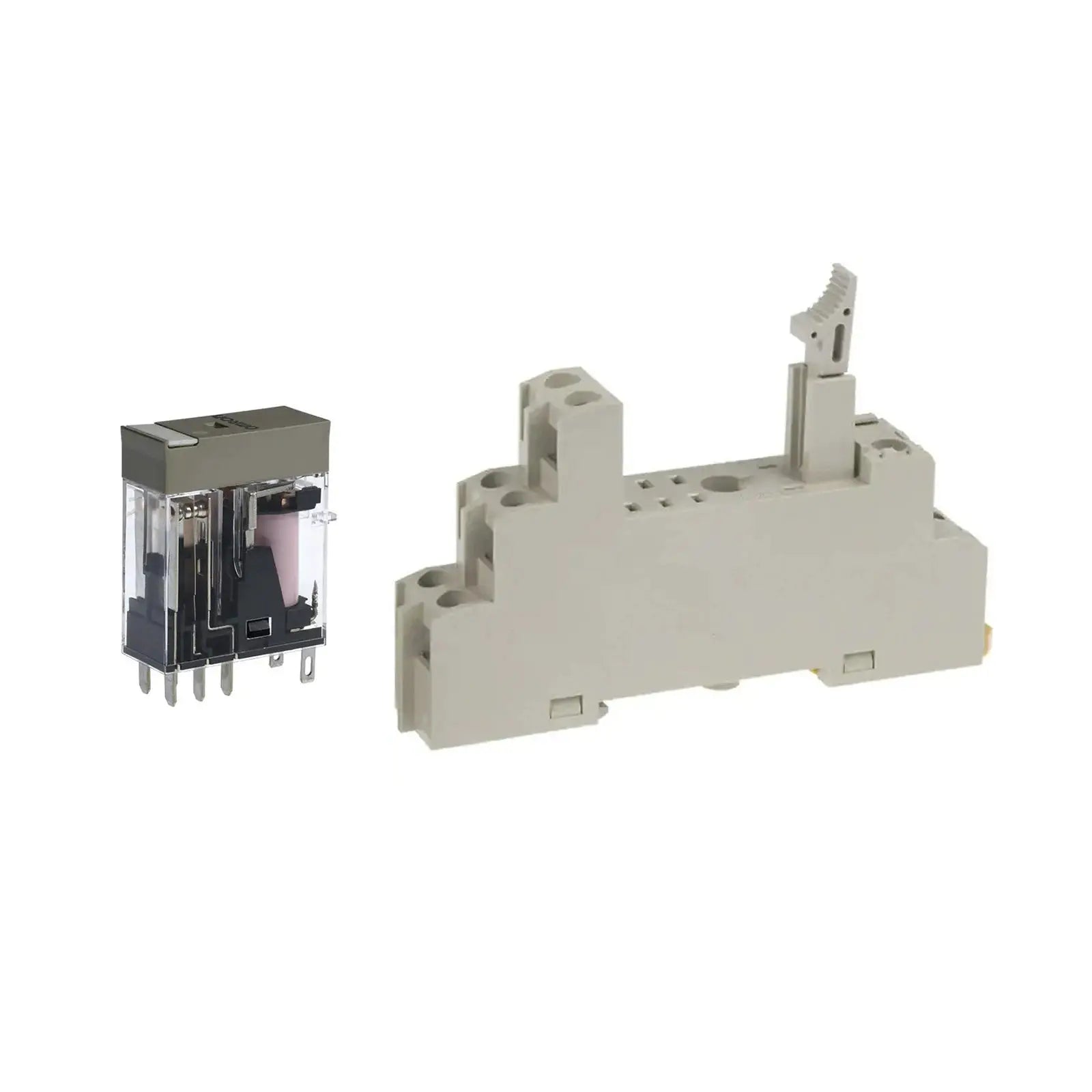

























































Relays for power distribution are essential electrical components designed to control high-voltage circuits with low-power signals. They provide safe, efficient, and automated switching in industrial, commercial, and electrical systems. Whether used in control panels, machinery, or energy management setups, these relays ensure precise operation and long-lasting reliability.
Why Choose Relays for Power Distribution?
Relays protect electrical systems from overload, short circuits, and operational faults while enabling remote and automated switching. They are vital in preventing equipment damage, reducing downtime, and improving energy efficiency. For industries where performance and safety are non-negotiable, high-quality relays deliver the dependable control needed to keep systems running smoothly.
How Our Relays Improve Your Systems
Our collection includes electromechanical, solid-state, and time-delay relays from trusted brands, built for demanding environments. With durable construction, accurate switching, and easy integration, these relays offer outstanding performance in power distribution networks and heavy-duty applications.
Need Bulk Orders or Expert Recommendations on PD-B-R?
Looking for bulk PD-B-R orders or need help choosing the right industrial solution? Our team is here to assist with custom quotes, product recommendations, and technical guidance. Whether you're an electrician, contractor, or business owner, we offer tailored solutions to meet your needs.
📩 Contact Us or chat with us live for instant assistance!
Explore Our Monthly Madness Deals Collection!
Don't miss out on huge savings across our store! Check out the best deals in:
Explore these categories now and grab the best deals before they're gone!
- All Products in Our Range – Top-quality products handpicked for you.
- Best Sellers – Customer favourites and high-demand items.
- Watts Hot Deals and Sales – Limited-time discounts on must-have products.
- Watts New – Fresh arrivals and the latest innovations.
-
All Collections – Explore everything we have to offer.
Explore these categories now and grab the best deals before they're gone!
Don't forget to Check out our Massive Markdowns While Stocks Last!
Recently viewed
Watts Current Newsletter
Stay connected with the latest industrial electrical products, exclusive deals, and expert updates.
Sign up now and never miss out