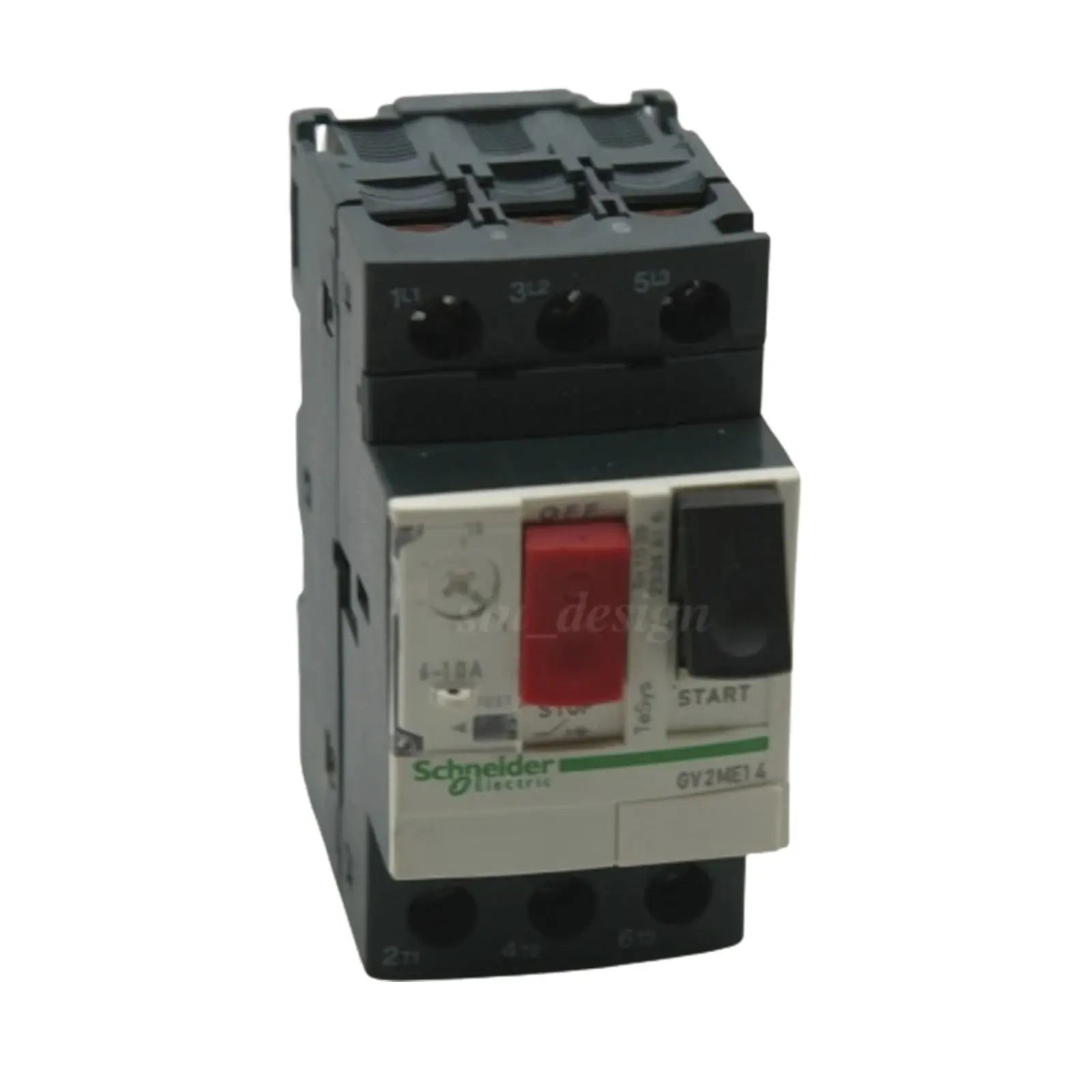
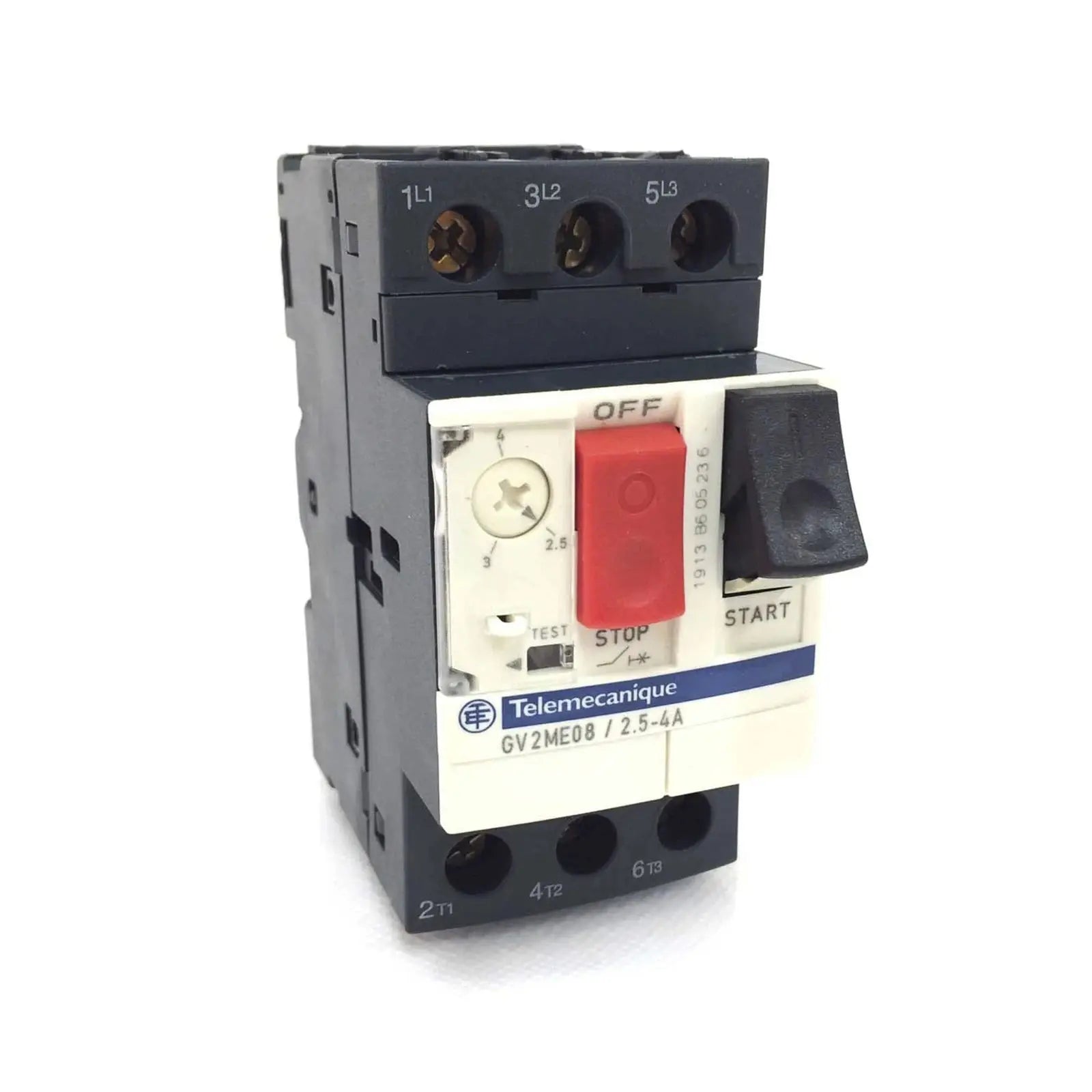
Démarreur de moteur : démarrage et contrôle des moteurs électriques
Comprendre les bases des démarreurs de moteurs
Pour comprendre l'importance des démarreurs de moteur, il est essentiel d'en comprendre les principes de base. Un démarreur est un dispositif qui déclenche et contrôle le fonctionnement d'un moteur électrique. Il joue un rôle crucial dans le démarrage en douceur et le fonctionnement sûr des moteurs. Examinons de plus près la définition et le fonctionnement des démarreurs de moteur, les différents types disponibles et les composants qui les composent.
Définition et fonction des démarreurs de moteur
Les démarreurs sont des dispositifs électriques qui fournissent le courant nécessaire au démarrage et au fonctionnement des moteurs à l'arrêt. Ils sont conçus pour protéger les moteurs des dommages potentiels dus à un courant excessif, à un déséquilibre de tension ou à une surchauffe. Leur fonction principale est de contrôler l'alimentation du moteur, garantissant ainsi un fonctionnement sûr et efficace.
Les démarreurs de moteur sont constitués d'une combinaison de contacteurs, de dispositifs de protection contre les surcharges, d'interrupteurs de commande, de fusibles et de relais de commande moteur. Le contacteur est le cœur du démarreur, chargé de connecter et de déconnecter le moteur de l'alimentation électrique. Les dispositifs de protection contre les surcharges, tels que les relais thermiques, surveillent le courant du moteur et le protègent contre la surchauffe en disjonctant le circuit si le courant dépasse une certaine limite.
Types de démarreurs de moteur
Il existe plusieurs types de démarreurs, chacun répondant à des exigences et des applications spécifiques. Les plus courants sont les démarreurs directs (DOL), les démarreurs étoile-triangle, les démarreurs à autotransformateur et les démarreurs progressifs. Le choix du démarreur dépend de facteurs tels que la taille du moteur, le courant de démarrage et les performances souhaitées.
Le démarreur direct (DOL) est le type de démarreur le plus simple et le plus courant. Il connecte directement le moteur à l'alimentation électrique, permettant un démarrage à pleine tension. Les démarreurs étoile-triangle, quant à eux, utilisent une série de contacteurs pour démarrer le moteur en configuration étoile basse tension, puis passent en configuration triangle haute tension une fois que le moteur atteint une certaine vitesse. Les démarreurs à autotransformateur assurent un démarrage en douceur et contrôlé grâce à un transformateur de tension variable qui augmente progressivement la tension d'alimentation du moteur. Les démarreurs progressifs, également appelés démarreurs statiques, utilisent des composants électroniques pour augmenter progressivement la tension et le courant d'alimentation du moteur, réduisant ainsi les contraintes sur le moteur lors du démarrage.
Composants d'un démarreur de moteur
Un démarreur moteur est composé de plusieurs composants essentiels, qui interagissent pour faciliter le démarrage et le contrôle du moteur. Ces composants comprennent des contacteurs, des dispositifs de protection contre les surcharges, des interrupteurs de commande, des fusibles et des relais de commande moteur. Chacun de ces composants joue un rôle unique dans le fonctionnement sûr et efficace des démarreurs et des moteurs.
Les contacteurs sont des dispositifs électromécaniques qui agissent comme des interrupteurs, autorisant ou interrompant le flux de courant vers le moteur. Les dispositifs de protection contre les surcharges, tels que les relais thermiques, surveillent le courant du moteur et le protègent de la surchauffe en disjonctant le circuit si le courant dépasse une certaine limite. Les interrupteurs de commande, tels que les boutons de démarrage et d'arrêt, permettent de contrôler manuellement le fonctionnement du moteur. Les fusibles sont des dispositifs de sécurité qui protègent le moteur et le démarreur contre les courts-circuits et les surintensités en fondant et en coupant le circuit lorsque le courant dépasse un certain niveau. Les relais de commande moteur servent à contrôler le fonctionnement du démarreur, offrant des fonctionnalités supplémentaires telles que l'inversion du sens de rotation du moteur ou le contrôle simultané de plusieurs moteurs.
Comprendre les bases des démarreurs de moteur est essentiel pour toute personne impliquée dans la conception, l'installation ou la maintenance de systèmes électriques. En choisissant le bon type de démarreur et en garantissant le bon fonctionnement de ses composants, vous garantissez un fonctionnement sûr et efficace des moteurs, prolongeant ainsi leur durée de vie et minimisant les risques d'arrêts coûteux.
Le rôle des démarreurs dans les moteurs électriques
Les démarreurs jouent un rôle essentiel dans le fonctionnement des moteurs électriques. Ils sont responsables du démarrage et du contrôle de la vitesse et du sens de rotation du moteur. Découvrons comment les démarreurs facilitent le démarrage et le contrôle des moteurs électriques, ainsi que leurs fonctions de sécurité.
Démarrage des moteurs électriques
Lorsqu'un moteur est alimenté, une surtension est nécessaire pour vaincre l'inertie et démarrer la rotation. Les démarreurs fournissent cette surtension initiale en appliquant momentanément une haute tension aux enroulements du moteur. Cela permet de démarrer le moteur et de le mettre en mouvement, lui permettant ainsi de fonctionner sans à-coups.
Contrôle des moteurs électriques
Outre le démarrage des moteurs, les démarreurs permettent également de contrôler leur fonctionnement. Ils permettent à l'utilisateur de démarrer, d'arrêter et de contrôler la vitesse et le sens de rotation du moteur. Ce contrôle est essentiel dans diverses applications, notamment les machines industrielles, les systèmes CVC et les systèmes de transport.
Caractéristiques de sécurité des démarreurs de moteur
Les démarreurs de moteur sont équipés de multiples dispositifs de sécurité pour assurer la protection du moteur et de l'utilisateur. Ces dispositifs comprennent une protection contre les surcharges, les courts-circuits, les sous-charges, la surchauffe et la surtension. En surveillant en permanence les conditions de fonctionnement du moteur, le démarreur peut détecter toute anomalie et prendre les mesures appropriées pour éviter tout dommage ou blessure.
La protection contre les surcharges est une caractéristique de sécurité importante des démarreurs de moteur. Cette fonction permet d'éviter d'endommager le moteur en surveillant le courant qui le traverse. Si le courant dépasse un certain seuil, le démarreur déconnecte automatiquement le moteur de la source d'alimentation, évitant ainsi toute surchauffe et tout dommage potentiel.
La protection contre les courts-circuits est une autre caractéristique de sécurité. En cas de court-circuit, lorsqu'un chemin de faible résistance est créé entre l'alimentation et le moteur, le démarreur détecte le courant excessif et interrompt rapidement le circuit. Cela protège le moteur et réduit les risques d'incendie et de dangers électriques.
Choisir le bon démarreur de moteur
Choisir le bon démarreur est crucial pour optimiser les performances et la longévité du moteur. Plusieurs facteurs doivent être pris en compte lors de la sélection d'un démarreur, notamment le type de moteur, sa taille, son environnement d'utilisation et les caractéristiques de contrôle moteur souhaitées. Examinons ces facteurs en détail pour comprendre comment prendre une décision éclairée.
En matière de démarreurs, il n'existe pas de solution universelle. Chaque moteur a des exigences spécifiques qu'il faut prendre en compte pour garantir un fonctionnement fluide et efficace. Examinons de plus près les facteurs à prendre en compte lors du choix d'un démarreur.
Facteurs à prendre en compte
Lors du choix d'un démarreur, il est important de prendre en compte des facteurs tels que les exigences de courant et de tension du moteur, la température ambiante de fonctionnement, le cycle de service et toute fonctionnalité supplémentaire requise pour des applications spécifiques. Ne pas tenir compte de ces facteurs peut entraîner un fonctionnement inefficace du moteur, une usure prématurée, voire une panne.
Examinons de plus près chacun de ces facteurs :
Exigences de courant et de tension : Le démarreur doit être capable de gérer les exigences de courant et de tension du moteur. Il est essentiel de choisir un démarreur capable de fournir le courant et la tension nécessaires au bon fonctionnement du moteur.
Température ambiante : L'environnement de fonctionnement joue un rôle important dans les performances du moteur. Des températures élevées peuvent affecter son efficacité et sa durée de vie. Il est important de choisir un démarreur capable de supporter la température ambiante de l'environnement dans lequel le moteur fonctionnera.
Cycle de service : Le cycle de service désigne la durée de fonctionnement du moteur par rapport à la durée totale. Les moteurs à cycle de service élevé nécessitent des démarreurs capables de supporter un fonctionnement continu sans surchauffe ni usure prématurée.
Fonctionnalités supplémentaires : Selon l'application spécifique, des fonctionnalités supplémentaires peuvent être requises. Par exemple, certains moteurs peuvent nécessiter une protection contre les surcharges, tandis que d'autres peuvent nécessiter des fonctions de contrôle pour un contrôle précis de la vitesse. Il est essentiel d'identifier ces exigences supplémentaires et de sélectionner un démarreur moteur capable d'y répondre.
Adaptation des démarreurs aux types de moteurs
Chaque moteur présente des caractéristiques et des exigences de démarrage différentes. Il est donc crucial d'adapter le démarreur à chaque type de moteur. Par exemple, les moteurs à induction peuvent bénéficier de démarreurs progressifs pour réduire la surintensité initiale, tandis que les moteurs synchrones peuvent nécessiter des fonctions de contrôle spécifiques pour se synchroniser avec le réseau électrique.
En sélectionnant un démarreur de moteur spécialement conçu pour le type de moteur, vous pouvez garantir des performances optimales et éviter tout problème potentiel pouvant survenir en raison de composants incompatibles.
Comprendre les valeurs nominales des démarreurs de moteurs
Les démarreurs de moteur sont proposés avec différentes puissances nominales et spécifications qui indiquent leurs capacités et leurs limites. Il est essentiel de bien comprendre ces puissances nominales, notamment le courant nominal maximal, la tension nominale et la résistance aux courts-circuits. Cette compréhension garantit le fonctionnement sûr et efficace du démarreur et du moteur connecté.
Lors du choix d'un démarreur, il est important de consulter les spécifications et les directives du fabricant afin de s'assurer que le démarreur choisi est compatible avec le moteur et répond à toutes les exigences requises. Prendre le temps de bien comprendre ces facteurs et de prendre une décision éclairée permettra d'optimiser les performances et la longévité du moteur.
Installation et maintenance des démarreurs de moteurs
Une installation correcte et un entretien régulier sont essentiels au fonctionnement fiable et efficace des démarreurs de moteur. Examinons le processus d'installation étape par étape et les pratiques d'entretien à suivre pour garantir la longévité de vos démarreurs.
Guide d'installation étape par étape
L'installation d'un démarreur moteur exige une attention particulière pour garantir son bon fonctionnement. Elle comprend le montage du démarreur, le raccordement du câblage électrique, la configuration des paramètres de commande et la réalisation de tests pour vérifier son bon fonctionnement. Suivre un guide étape par étape vous permettra d'éviter les erreurs d'installation et de garantir une installation réussie.
Commencez par choisir un emplacement approprié pour le démarreur. Il doit être installé dans un endroit bien ventilé, à l'abri de la chaleur excessive, de l'humidité et des substances corrosives. Fixez le démarreur solidement à l'aide des supports ou des trous de fixation fournis, en veillant à ce qu'il soit de niveau et stable.
Ensuite, connectez soigneusement le câblage électrique conformément aux instructions du fabricant. Cela comprend le raccordement des câbles d'alimentation, du moteur et du circuit de commande. Il est essentiel d'utiliser des fils de section appropriée et de garantir une isolation et des terminaisons adéquates pour éviter les risques électriques et garantir un fonctionnement fiable.
Une fois le câblage terminé, configurez les paramètres de commande du démarreur. Cela peut impliquer d'ajuster des paramètres tels que les paramètres de protection du moteur, les méthodes de démarrage et d'arrêt, et les entrées de commande. Consultez la documentation du démarreur pour obtenir des instructions précises sur la configuration précise de ces paramètres.
Une fois l'installation terminée, il est essentiel d'effectuer des tests pour vérifier le fonctionnement du démarreur. Cela comprend la vérification de la rotation du moteur, de sa bonne réponse aux commandes et des performances du moteur sous différentes conditions de charge. Toute anomalie ou problème doit être résolu rapidement avant la mise en service normale du démarreur.
Pratiques d'entretien de routine
Les démarreurs de moteur, comme tout autre appareil électrique, nécessitent un entretien régulier pour préserver leurs performances et prolonger leur durée de vie. Leur entretien régulier comprend l'inspection et le nettoyage des composants, la vérification des connexions électriques, la lubrification des pièces mobiles et la réalisation de tests périodiques pour garantir leur bon fonctionnement. Ces pratiques permettent d'identifier et de résoudre les problèmes avant qu'ils ne s'aggravent et ne provoquent des complications majeures.
Commencez par inspecter visuellement le démarreur pour détecter tout signe de dommage, comme des connexions desserrées ou corrodées, des composants usés ou une surchauffe. Nettoyez le démarreur à l'aide d'une brosse douce ou d'air comprimé pour éliminer la poussière, la saleté ou les débris qui pourraient nuire à son fonctionnement.
Vérifiez ensuite les connexions électriques pour vous assurer qu'elles sont bien serrées et sécurisées. Des connexions desserrées peuvent entraîner des chutes de tension, une surchauffe et des risques électriques potentiels. Resserrez les connexions desserrées et inspectez le câblage pour détecter tout signe d'usure ou de dommage nécessitant une réparation ou un remplacement.
Lubrifiez les pièces mobiles du démarreur, telles que les contacteurs et les relais, avec un lubrifiant approprié recommandé par le fabricant. Cela permet de réduire les frottements, d'éviter une usure excessive et d'assurer un fonctionnement fluide. Veillez à respecter les instructions du fabricant concernant le type et la fréquence de lubrification.
Effectuez régulièrement des tests pour vous assurer du bon fonctionnement du démarreur. Cela peut inclure la vérification du temps de réponse du démarreur, la vérification de l'exactitude des réglages de protection du moteur et la réalisation de tests de résistance d'isolement. Ces tests permettent d'identifier les problèmes potentiels et de prendre rapidement des mesures correctives.
Dépannage des problèmes courants
Malgré une installation et un entretien appropriés, les démarreurs de moteur peuvent rencontrer des problèmes de temps à autre. Parmi les problèmes courants, on trouve des contacteurs défectueux, des fusibles grillés, une surcharge du moteur ou un câblage incorrect. Comprendre comment résoudre ces problèmes et identifier leurs causes profondes peut contribuer à les résoudre efficacement et à minimiser les temps d'arrêt.
Si un moteur ne démarre pas, il est essentiel de vérifier l'alimentation et de s'assurer que le démarreur reçoit la tension adéquate. Inspectez les contacteurs pour détecter tout signe de dommage ou d'usure et remplacez-les si nécessaire. Des fusibles grillés peuvent indiquer un court-circuit ou une surcharge ; il est donc crucial d'identifier et de traiter la cause sous-jacente avant de remplacer le fusible.
En cas de surcharge du moteur, vérifiez les conditions de charge du moteur et assurez-vous qu'elles respectent les limites spécifiées. Ajustez les paramètres de protection du moteur si nécessaire pour éviter les surcharges récurrentes. Un câblage incorrect peut entraîner un comportement anormal du moteur ou un défaut de démarrage. Inspectez soigneusement les connexions et corrigez toute erreur ou connexion desserrée.
Lors du dépannage des démarreurs de moteur, il est conseillé de consulter la documentation du fabricant ou de demander l'aide d'un technicien qualifié pour garantir un diagnostic précis et une résolution du problème.
En conclusion, les démarreurs sont des dispositifs essentiels pour le démarrage et le contrôle des moteurs électriques. Ils garantissent un fonctionnement sûr et efficace du moteur tout en le protégeant des dommages potentiels. Comprendre les principes de base des démarreurs, choisir le bon modèle et suivre les bonnes pratiques d'installation et de maintenance sont des étapes cruciales pour optimiser les performances et la longévité des moteurs. Grâce à ces pratiques, les démarreurs et les moteurs électriques fonctionneront de manière fluide et fiable pendant de nombreuses années.
Besoin de commandes en gros ou de recommandations d'experts sur MCE-B-MS ?
Vous souhaitez commander des MCE-B-MS en gros ou avez besoin d'aide pour choisir la solution industrielle idéale ? Notre équipe est là pour vous aider avec des devis personnalisés, des recommandations de produits et des conseils techniques. Que vous soyez électricien, entrepreneur ou chef d'entreprise, nous proposons des solutions sur mesure pour répondre à vos besoins.
📩 Contactez-nous ou discutez avec nous en direct pour une assistance instantanée !
Découvrez notre collection mensuelle d'offres de folie !
Profitez de réductions exceptionnelles dans notre magasin ! Découvrez les meilleures offres :
Explorez ces catégories maintenant et profitez des meilleures offres avant qu'elles ne disparaissent !
-
Tous les produits de notre gamme – Des produits de qualité supérieure sélectionnés avec soin pour vous.
-
Meilleures ventes – Articles préférés des clients et articles très demandés.
-
Offres spéciales et soldes Watts – Remises à durée limitée sur des produits incontournables.
-
Watts New – Nouveautés et dernières innovations.
-
Toutes les collections – Explorez tout ce que nous avons à offrir.
Explorez ces catégories maintenant et profitez des meilleures offres avant qu'elles ne disparaissent !
N'oubliez pas de consulter nos remises massives jusqu'à épuisement des stocks !